Background about the 7th Pay Commission:
The 7th Pay Commission was formed by the UPA Government in February 2014 and it was headed by Justice A K Mathur. It's members included Vivek Rae (Retired IAS Officer), Rathin Roy (Economist) and Meena Agarwal who was secretary of the commission. The recommendations are likely to benefit 55Lac Pensioners and 48Lac Central Govt Employees.
These recommendation have been suggested to Implemented from 01.01.2016 for all Central Govt and Military Employees respectively based on there existing Pay Scale.
Minimum Pay: This has been defined by the 7th Pay Commission based on the Aykroyd formula. Minimum pay has been recommended to be set at ₹18,000 per month.
Maximum Pay: The upper limit scale for a Central Govt Employees has also been defined and set at ₹2,25,000 per month for the Apex Scale and ₹2,50,000 per month for officers of the rank of Cabinet Secretary and others presently at the same pay level.
Fitment: A fitment factor of 2.57 is being proposed to be applied uniformly for all employees.
Annual Increment: The rate of annual increment is being retained at 3 percent.
Modified Assured Career Progression (MACP):
Performance benchmarks for MACP have been made more stringent from “Good” to “Very Good”.
The Commission has also proposed that annual increments not be granted in the case of those employees who are not able to meet the benchmark either for MACP or for a regular promotion in the first 20 years of their service.
No other changes in MACP recommended.
Military Service Pay (MSP): The Military Service Pay, which is a compensation for the various aspects of military service, will be admissible to the Defence forces personnel only. As before, Military Service Pay will be payable to all ranks up to and inclusive of Brigadiers and their equivalents. The current MSP per month and the revised rates recommended are as follows:
|
Present
|
Proposed
|
i.
|
Service Officers
|
₹6,000
|
₹15,500
|
ii.
|
Nursing Officers
|
₹4,200
|
₹10,800
|
iii.
|
JCO/ORs
|
₹2,000
|
₹ 5,200
|
iv.
|
Non Combatants (Enrolled) in the Air Force
|
₹1,000
|
₹ 3,600
|
Short Service Commissioned Officers: Short Service Commissioned Officers will be allowed to exit the Armed Forces at any point in time between 7 and 10 years of service, with a terminal gratuity equivalent of 10.5 months of reckonable emoluments. They will further be entitled to a fully funded one year Executive Programme or a M.Tech. programme at a premier Institute.
Lateral Entry/Settlement: The Commission is recommending a revised formulation for lateral entry/resettlement of defence forces personnel which keeps in view the specific requirements of organization to which such personnel will be absorbed. For lateral entry into CAPFs an attractive severance package has been recommended.
Headquarters/Field Parity: Parity between field and headquarters staff recommended for similar functionaries e.g Assistants and Stenos.
Cadre Review: Systemic change in the process of Cadre Review for Group A officers recommended.
Allowances: The Commission has recommended abolishing 52 allowances altogether. Another 36 allowances have been abolished as separate identities, but subsumed either in an existing allowance or in newly proposed allowances. Allowances relating to Risk and Hardship will be governed by the proposed Risk and Hardship Matrix.
Risk and Hardship Allowance: Allowances relating to Risk and Hardship will be governed by the newly proposed nine-cell Risk and Hardship Matrix, with one extra cell at the top, viz., RH-Max to include Siachen Allowance.
The current Siachen Allowance per month and the revised rates recommended are as follows:
|
|
Present
|
Proposed
|
i.
|
Service Officers
|
₹21,000
|
₹31,500
|
iii.
|
JCO/ORs
|
₹14,000
|
₹21,000
|
This would be the ceiling for risk/hardship allowances and there would be no individual RHA with an amount higher than this allowance.
House Rent Allowance: Since the Basic Pay has been revised upwards, the Commission recommends that HRA be paid at the rate of 24 percent, 16 percent and 8 percent of the new Basic Pay for Class X, Y and Z cities respectively. The Commission also recommends that the rate of HRA will be revised to 27 percent, 18 percent and 9 percent respectively when DA crosses 50 percent, and further revised to 30 percent, 20 percent and 10 percent when DA crosses 100 percent.
In the case of PBORs of Defence, CAPFs and Indian Coast Guard compensation for housing is presently limited to the authorised married establishment hence many users are being deprived. The HRA coverage has now been expanded to cover all.
Any allowance not mentioned in the report shall cease to exist.
Emphasis has been placed on simplifying the process of claiming allowances.
Advances:
All non-interest bearing Advances have been abolished.
Regarding interest-bearing Advances, only Personal Computer Advance and House Building Advance (HBA) have been retained. HBA ceiling has been increased to ₹25 lakhs from the present ₹7.5 lakhs.
Central Government Employees Group Insurance Scheme (CGEGIS): The Rates of contribution as also the insurance coverage under the CGEGIS have remained unchanged for long. They have now been enhanced suitably. The following rates of CGEGIS are recommended:
|
Present
|
Proposed
|
Level of Employee
|
Monthly Deduction
(₹)
|
Insurance Amount
(₹)
|
Monthly Deduction
(₹)
|
Insurance Amount
(₹)
|
10 and above
|
120
|
1,20,000
|
5000
|
50,00,000
|
6 to 9
|
60
|
60,000
|
2500
|
25,00,000
|
1 to 5
|
30
|
30,000
|
1500
|
15,00,000
|
Medical Facilities:
Introduction of a Health Insurance Scheme for Central Government employees and pensioners has been recommended.
Meanwhile, for the benefit of pensioners residing outside the CGHS areas, CGHS should empanel those hospitals which are already empanelled under CS (MA)/ECHS for catering to the medical requirement of these pensioners on a cashless basis.
All postal pensioners should be covered under CGHS. All postal dispensaries should be merged with CGHS.
Pension: The Commission recommends a revised pension formulation for civil employees including CAPF personnel as well as for Defence personnel, who have retired before 01.01.2016. This formulation will bring about parity between past pensioners and current retirees for the same length of service in the pay scale at the time of retirement.
The past pensioners shall first be fixed in the Pay Matrix being recommended by the Commission on the basis of Pay Band and Grade Pay at which they retired, at the minimum of the corresponding level in the pay matrix.
This amount shall be raised to arrive at the notional pay of retirees, by adding number of increments he/she had earned in that level while in service at the rate of 3 percent.
In the case of defence forces personnel this amount will include Military Service Pay as admissible.
Fifty percent of the total amount so arrived at shall be the new pension.
An alternative calculation will be carried out, which will be a multiple of 2.57 times of the current basic pension.
The pensioner will get the higher of the two.
Gratuity: Enhancement in the ceiling of gratuity from the existing ₹10 lakh to ₹20 lakh. The ceiling on gratuity may be raised by 25 percent whenever DA rises by 50 percent.
Disability Pension for Armed Forces: The Commission is recommending reverting to a slab based system for disability element, instead of existing percentile based disability pension regime.
Ex-gratia Lump sum Compensation to Next of Kin: The Commission is recommending the revision of rates of lump sum compensation for next of kin (NOK) in case of death arising in various circumstances relating to performance of duties, to be applied uniformly for the defence forces personnel and civilians including CAPF personnel.
Martyr Status for CAPF Personnel: The Commission is of the view that in case of death in the line of duty, the force personnel of CAPFs should be accorded martyr status, at par with the defence forces personnel.
New Pension System: The Commission received many grievances relating to NPS. It has recommended a number of steps to improve the functioning of NPS. It has also recommended establishment of a strong grievance redressal mechanism.
Regulatory Bodies: The Commission has recommended a consolidated pay package of ₹4,50,000 and ₹4,00,000 per month for Chairpersons and Members respectively of select Regulatory bodies. In case of retired government servants, their pension will not be deducted from their consolidated pay. The consolidated pay package will be raised by 25 percent as and when Dearness Allowance goes up by 50 percent. For Members of the remaining Regulatory bodies normal replacement pay has been recommended.
Performance Related Pay: The Commission has recommended introduction of the Performance Related Pay (PRP) for all categories of Central Government employees, based on quality Results Framework Documents, reformed Annual Performance Appraisal Reports and some other broad Guidelines. The Commission has also recommended that the PRP should subsume the existing Bonus schemes.
There are few recommendations of the Commission where there was no unanimity of view and these are as follows:
The Edge: An edge is presently accordeded to the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) and the Indian Foreign Service (IFS) at three promotion stages from Senior Time Scale (STS), to the Junior Administrative Grade (JAG) and the NFSG. is recommended by the Chairman, to be extended to the Indian Police Service (IPS) and Indian Forest Service (IFoS).
Shri Vivek Rae, Member is of the view that financial edge is justified only for the IAS and IFS. Dr. Rathin Roy, Member is of the view that the financial edge accorded to the IAS and IFS should be removed.
Empanelment: The Chairman and Dr. Rathin Roy, Member, recommend that All India Service officers and Central Services Group A officers who have completed 17 years of service should be eligible for empanelment under the Central Staffing Scheme and there should not be “two year edge”, vis-à-vis the IAS. Shri Vivek Rae, Member, has not agreed with this view and has recommended review of the Central Staffing Scheme guidelines.
Non Functional Upgradation for Organised Group ‘A’ Services: The Chairman is of the view that NFU availed by all the organised Group `A’ Services should be allowed to continue and be extended to all officers in the CAPFs, Indian Coast Guard and the Defence forces. NFU should henceforth be based on the respective residency periods in the preceding substantive grade. Shri Vivek Rae, Member and Dr. Rathin Roy, Member, have favoured abolition of NFU at SAG and HAG level.
Superannuation: Chairman and Dr. Rathin Roy, Member, recommend the age of superannuation for all CAPF personnel should be 60 years uniformly. Shri Vivek Rae, Member, has not agreed with this recommendation and has endorsed the stand of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
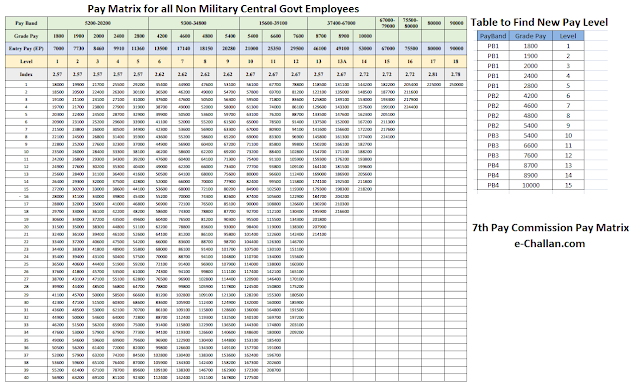
Please find below the Pay Matrix you can use to Calculate Salary or Pension based on the recommendations.
 |
| 7th Pay Commission Calculator |